
About...
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is a narrowing of the peripheral arteries to the legs, stomach, arms, and head – most commonly in the arteries of the legs.
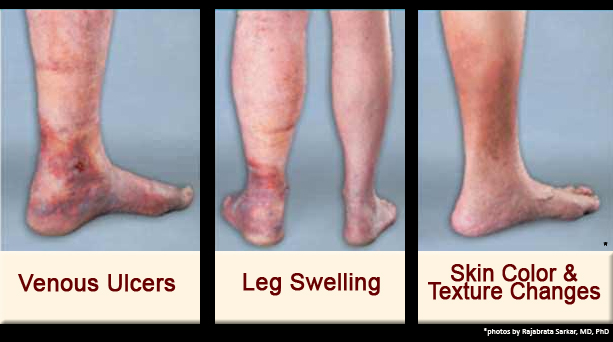
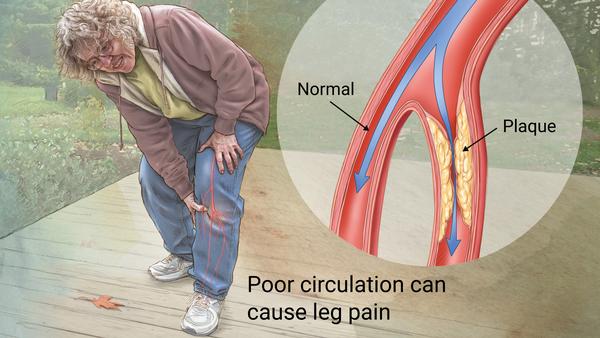
When you develop peripheral artery disease (PAD), your extremities — usually your legs — don’t receive enough blood flow to keep up with demand. This causes symptoms, most notably leg pain when walking (claudication).
Peripheral artery disease is also likely to be a sign of a more widespread accumulation of fatty deposits in your arteries (atherosclerosis). This condition may be reducing blood flow to your heart and brain, as well as your legs.
The most common symptoms of PAD involving the lower extremities are cramping, pain or tiredness in the leg or hip muscles while walking or climbing stairs. Typically, this pain goes away with rest and returns when you walk again.
People with peripheral arterial disease have a higher risk of coronary artery disease, heart attack or stroke.
Left untreated, PAD can lead to gangrene and amputation.
Vascular Centers of Michigan Areas of Expertise:
- Angiogram (pictures taken of the peripheral vascular system)
- Angioplasty (PTA or percutaneous transluminal angioplasty is an interventional procedure where a balloon is placed at the site of a blockage and inflated and then removed to open up the blockage)
- Atherectomy (Is when were actually physically remove the plaque for the arteries. This requires a special device.)
- Stenting (Is like an Angioplasty but we us a wire mesh called a stent to leek the artery open)
- IVUS (Inter Vascular UltraSound- is a device used to measure blockages during the procedure)

Before and After
is complete or almost complete blockage
of a coronary artery for 30 or more days.
Coronary CTO is caused by a heavy build-up
of atherosclerotic plaque within the artery.

Before and After